In poor lighting conditions, our eyes struggle to distinguish details, making it difficult for us to see what’s around us. This challenge is even greater when we are tired or stressed, as our vision becomes even less reliable.
NIGHT VISION (NVS): WHAT IS IT?
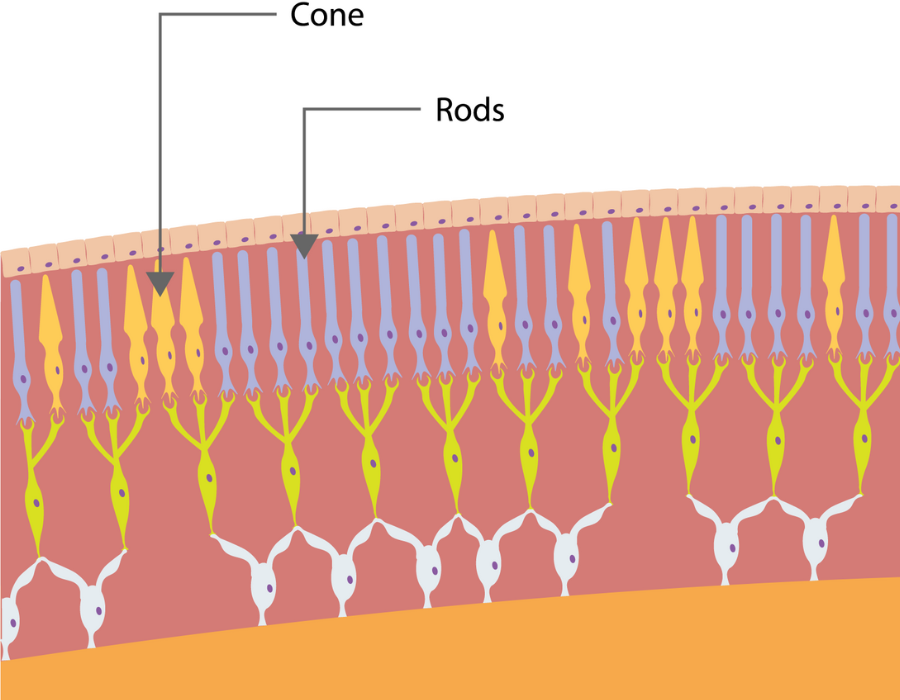
Did you know that the human eye operates on three levels?
- Daytime vision “photopic”
- Intermediate vision “mesopic”
- Night vision “scotopic”
As light diminishes, only the rods, which are much more sensitive than cones, react. There are between 92 to 100 million rods in humans (compared to approximately 150 million in cats, which have night vision). This explains why our vision switches to black and white in darkness. Additionally, objects appear blurry because the transmission of signals from rods to the optic nerve is less efficient than cones. Essentially, to activate night vision and allow residual low light to pass through, the pupil dilates and stimulates the rods. However, this capacity has its limitations and doesn’t enable very effective night vision.
This is why, at the beginning of the twentieth century, humans sought to develop night vision technology, driven by the need to improve visibility in low light conditions. Early developments focused on image intensification, a process that collects and amplifies available light to produce visible images. This fundamental technology laid the foundations for the creation of night vision devices capable of illuminating the darkness and revealing environments then unknown to the human eye.
SPECIAL TECHNOLOGIES FOR NIGHT VISION (NVS)
Night vision devices primarily function by amplifying the available light in the environment, enabling the user to see in darkness. These devices capture photons of available light, even at very low levels, and amplify them to produce a visible image for the user.
Why does night vision use infrared light ?
Some night vision devices also utilize infrared emitters to illuminate the environment. These emitters produce infrared light that is invisible to the human eye but detectable by the sensors of the night vision device. This creates a visible image even in total darkness. The use of infrared light in night vision allows for seeing in conditions where visible light is absent.
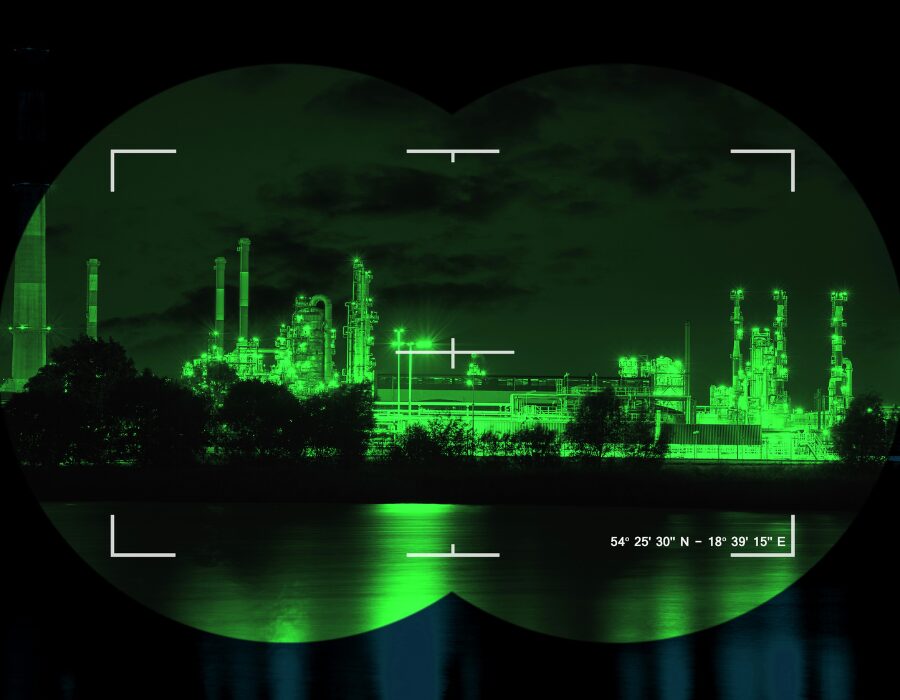

Why are night vision goggles green ?
The green tint of night vision goggles is a result of how light intensifier tubes convert light. Photons of light are converted into electrons, which are then amplified. The green tint comes from the conversion of electrons into visible light photons. This green hue provides high contrast and good detail perception in darkness, which is particularly useful in low-light conditions.
WHAT KIND OF APPLICATIONS NIGHT VISION IS USED FOR?
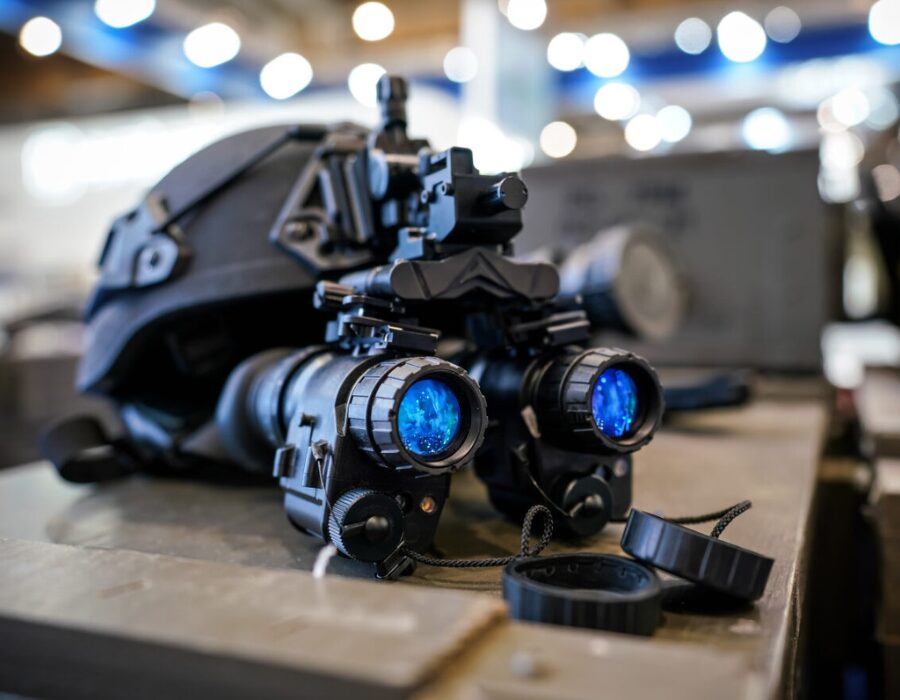
Defense has long been a driving force behind the development and deployment of night vision technology, utilizing it to gain a strategic advantage in nocturnal operations enhancing situational awareness and operational effectiveness on the battlefield. From night vision goggles to thermal imaging scopes, these advanced devices allow operators to complete reconnaissance, navigation and engagement with confidence and in safety under the cover of darkness.


While night vision technology has its roots in military applications, its impact extends far beyond the confines of the battlefield. Consumers of electronics use night vision and integrate it into everyday devices, such as vehicles and cameras. Automotive manufacturers leverage night vision systems to improve driver visibility and safety, while outdoor enthusiasts use cameras for wildlife observation and night-time exploration.
The evolution and applications of night vision technology have transformed our ability to perceive and navigate the darkness, opening up new possibilities across various industries. From military operations to consumer electronics, the impact of night vision is profound and far-reaching. APEM has been integrating this innovative technology into its field of expertise for years, and we encourage you to discover our QRM-NV LED.
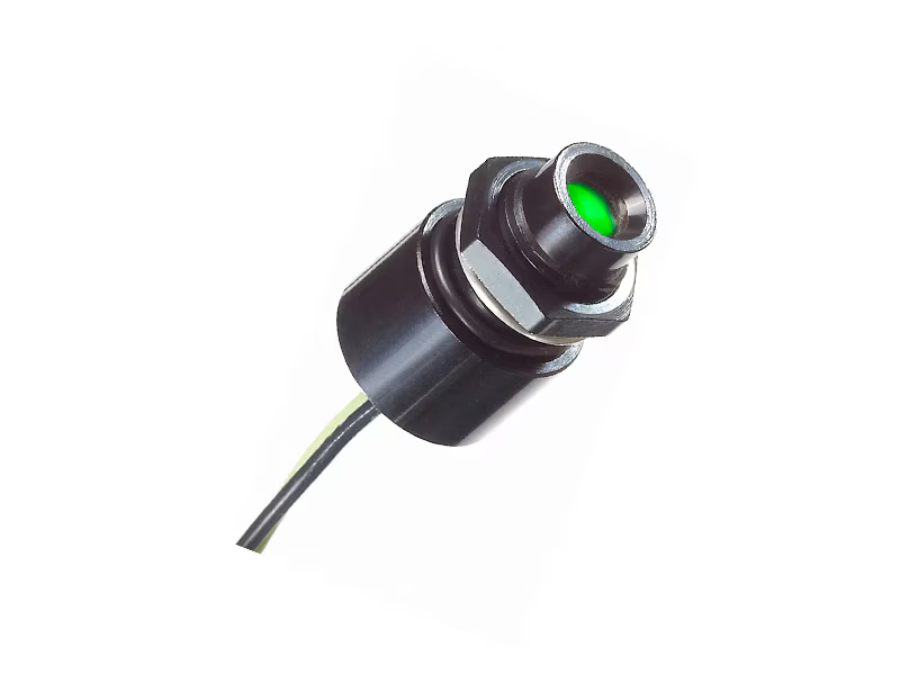
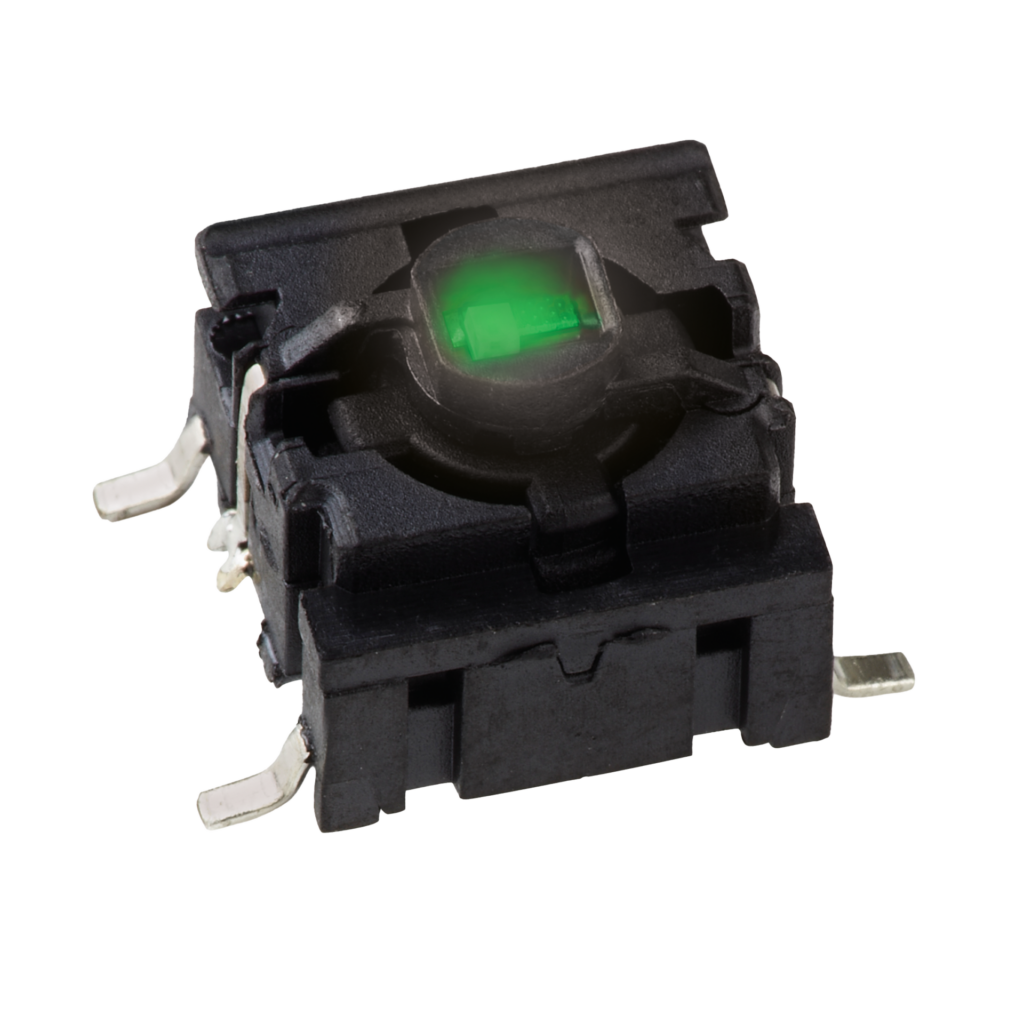
APEM’S NIGHT VISION COMPATIBLE SOLUTIONS: QRM LED INDICATOR & MEC 5G SWITCH
APEM offers cutting-edge solutions for night operations with the QRM-NV LED indicator and MEC 5G tactile switch, both designed for defense and critical applications. The QRM-NV indicator, NVG-compatible and NVIS-compliant to MIL-STD-3009, ensures clear visibility in low-light conditions, enhancing situational awareness in sectors like defense, security, and marine. Complementing this, the MEC 5G series is a fully customizable switch with a night vision option, adapting to any tactical configuration. Whether integrated discreetly under a membrane or used as a stand-alone solution, it delivers optimal ergonomics, IP67 sealing, and a 10-million-cycle lifespan. Engineered for durability, it withstands forces up to 115N (MIL-PRF-22885H), ensuring reliable performance.





